Avulsion Fractures Medial And Lateral Malleoli Image Radiopaedia Org

Avulsion Fractures Medial And Lateral Malleoli Image Radiopaedia Org Age: 30 years. gender: male. medial malleolus avulsion fracture. x ray. anteromedial soft tissue swelling. small ankle joint effusion. mildly displaced avulsion fracture from the tip of the medial malleolus in keeping with a deltoid ligament injury. small fleck lying posterior to the posterior malleolus may represent a further avulsion fracture. Patel m, avulsion fractures of medial and lateral malleoli. case study, radiopaedia.org (accessed on 24 jan 2024) doi.org 10.53347 rid 10902.
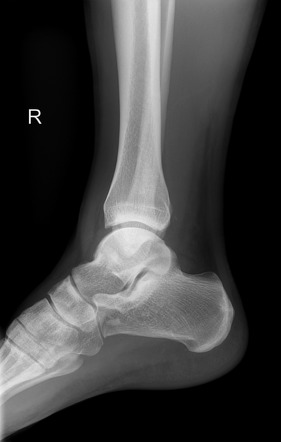
Medial Malleolus Avulsion Fracture Image Radiopaedia Org Weber b fractures could be further subclassified as 9. b1: isolated. b2: associated with a medial lesion (malleolus or ligament) b3: associated with a medial lesion and fracture of posterolateral tibia. type c. above the level of the syndesmosis (suprasyndesmotic) tibiofibular syndesmosis disruption with widening of the distal tibiofibular. Ankle tendon attachment. an avulsion fracture is where a fragment of bone is pulled away at the ligamentous or tendinous attachment. it can be caused by traumatic traction (repetitive long term or a single high impact traumatic traction) of the ligament or tendon. an avulsion fracture occurs because tendons can bear more load than the bone. An avulsion fracture is caused by tension on the bifurcate ligament during forceful inversion and plantar flexion of the foot. in fact, this fracture constitutes the most common avulsion fracture affecting the calcaneus [26]. in general, impaction fractures tend to be larger than avulsion fractures. Ottawa ankle rules (sen 96 99% for excluding fracture) 3 views: ap: best for isolated lateral and medial malleolar fractures. oblique (mortise) best for evaluating for unstable fracture or soft tissue injury. at a point 1 cm proximal to tibial plafond space between tib fib should be ≤6mm. lateral: best for posterior malleolar fractures.

Comments are closed.