Can You Use Contractions In Formal Writing A Comprehensive Guide The

Can You Use Contractions In Formal Writing A Comprehensive Guide The In the middle of the spectrum you have things like these blog posts. on the formal end of the spectrum, you have the scholarly writing you do for classroom assignments, theses and dissertations, and publications. contractions are a part of informal writing. thus, avoid contractions in scholarly writing, except for under the following circumstances:. Contractions in writing and speaking are formed by combining two or more other words into one. when writing contractions, an apostrophe replaces the missing letter (s) and the space between the original words disappears. most common contractions represent a pronoun a verb (be, have, would), or a verb ‘not’.

Can You Use Contractions In Formal Writing A Comprehensive Guide The Contractions, which are words in which some letters or sounds are omitted (e.g., don’t for do not), are common in speech and informal usage but generally avoided in formal writing. examples. informal: we don’t know what happened. formal: we do not have sufficient information yet to form a hypothesis. contractions in informal vs. formal usage. Contractions, especially the ‘s contraction, are common with question words, such as “who” or “what”, as well as with “that”, “there” and “here”. you can also use contractions with nouns. just like with question words, the ‘s contraction is used a lot. here are a few examples: dave’s going to come over later = dave is. The most common type of contraction is the combination of a subject pronoun (e.g., i, she, they) and a verb (e.g., have, are, is). let’s look at a few examples: we are going to the store. → we’re going to the store. i am five minutes away. → i’m five minutes away. she is starting a new job. → she’s starting a new job. The teacher’s key to the classroom and can’t be replaced. this phrase could be read as possessive, the key the teacher owns, instead of the verb to be, the teacher is. cambridge dictionary: “contractions are usually not appropriate in formal writing.”. australian government style guide: “contractions are shortened words.
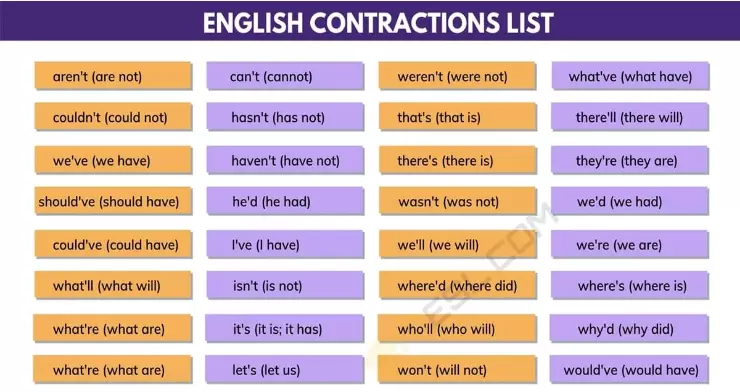
Can You Use Contractions In Essays College Or Formal Writing The most common type of contraction is the combination of a subject pronoun (e.g., i, she, they) and a verb (e.g., have, are, is). let’s look at a few examples: we are going to the store. → we’re going to the store. i am five minutes away. → i’m five minutes away. she is starting a new job. → she’s starting a new job. The teacher’s key to the classroom and can’t be replaced. this phrase could be read as possessive, the key the teacher owns, instead of the verb to be, the teacher is. cambridge dictionary: “contractions are usually not appropriate in formal writing.”. australian government style guide: “contractions are shortened words. This article provides a comprehensive guide to understanding contractions in formal writing. it explains the rules of grammar, provides examples of how to properly use contractions, and offers tips on when and how to appropriately use them in formal writing. The purpose of contractions is to streamline sentences and convey a more informal tone often used in spoken language. most contractions consist of a pronoun or a modal verb and an auxiliary verb. for example, “she will” becomes “she’ll,” and “cannot” becomes “can’t.”. the apostrophe marks where letters have been omitted.

Comments are closed.