Electromagnetic Waves Definition Propagation And Types
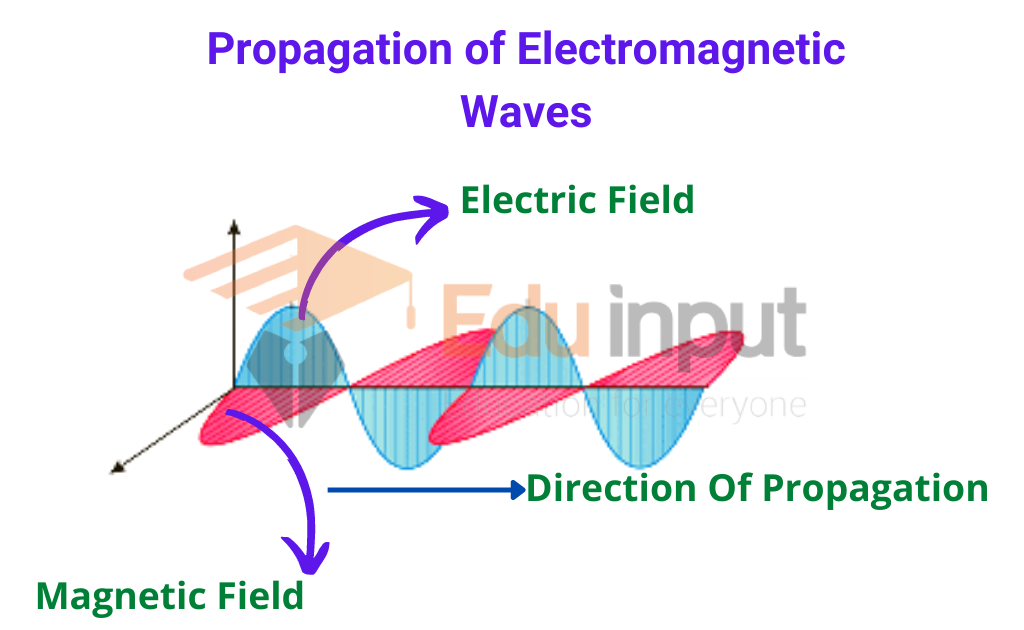
Electromagnetic Waves Definition Propagation And Types Electromagnetic (em) waves, also called electromagnetic radiation, are created by the coupling of oscillating electric and magnetic fields, whose directions are perpendicular to each other. the direction of propagation of the em wave is perpendicular to both the electric and magnetic field vectors. unlike mechanical waves, electromagnetic waves. Electromagnetic waves. electromagnetic radiation, is a form of energy emitted by moving charged particles. as it travels through space it behaves like a wave, and has an oscillating electric field component and an oscillating magnetic field. these waves oscillate perpendicularly to and in phase with one another.
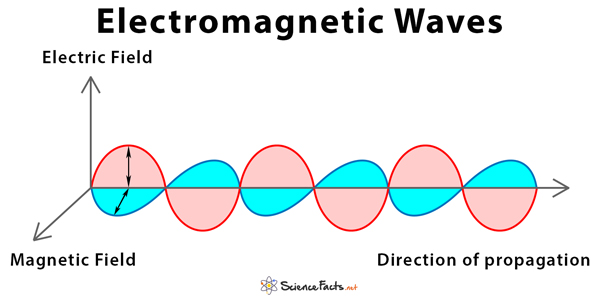
Electromagnetic Waves Definition Propagation And Types In homogeneous, isotropic media, the oscillations of the two fields are on average perpendicular to each other and perpendicular to the direction of energy and wave propagation, forming a transverse wave. electromagnetic radiation is commonly referred to as "light", em, emr, or electromagnetic waves. [2] the position of an electromagnetic wave. Electromagnetic radiation, in classical physics, the flow of energy at the universal speed of light through free space or through a material medium in the form of the electric and magnetic fields that make up electromagnetic waves such as radio waves, visible light, and gamma rays. in such a wave, time varying electric and magnetic fields are. The electromagnetic wave equation describes the propagation of electromagnetic waves in a vacuum or through a medium. the electromagnetic wave equation is a second order partial differential equation. it is a 3d form of the wave equation. the homogeneous form of the equation is written as. 57012. konstantin k. likharev. stony brook university. this (rather extensive) chapter focuses on the most important effect that follows from the time dependent maxwell equations, namely the electromagnetic waves, at this stage avoiding a discussion of their origin, i.e. the radiation process – which will the subject of chapters 8 and 10.
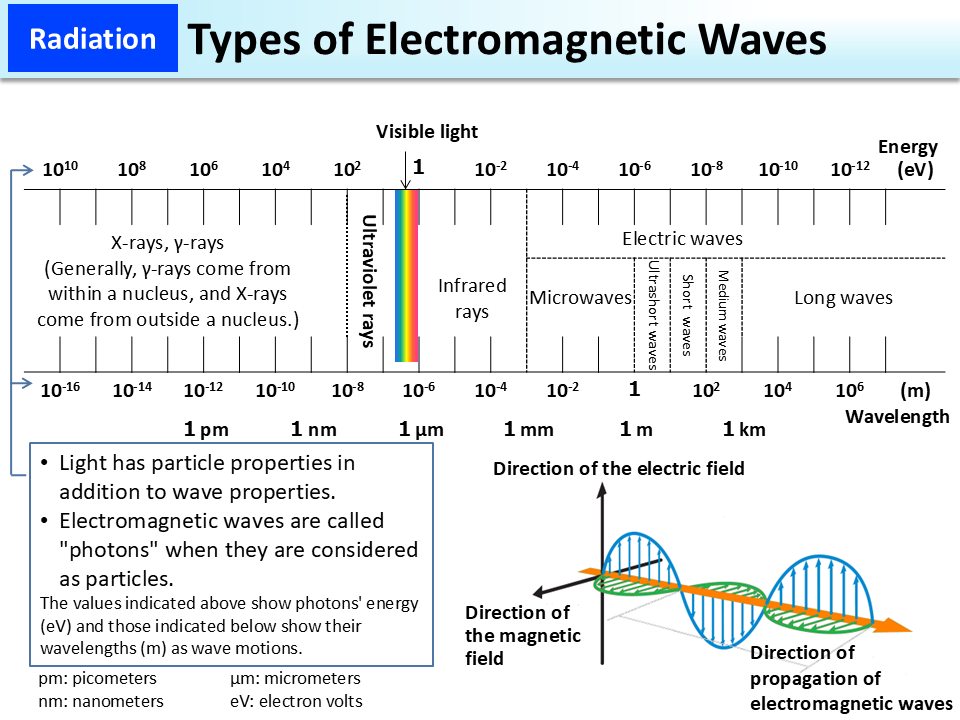
Types Of Electromagnetic Waves Moe The electromagnetic wave equation describes the propagation of electromagnetic waves in a vacuum or through a medium. the electromagnetic wave equation is a second order partial differential equation. it is a 3d form of the wave equation. the homogeneous form of the equation is written as. 57012. konstantin k. likharev. stony brook university. this (rather extensive) chapter focuses on the most important effect that follows from the time dependent maxwell equations, namely the electromagnetic waves, at this stage avoiding a discussion of their origin, i.e. the radiation process – which will the subject of chapters 8 and 10. Electromagnetic waves have two components: an oscillating electric field and a perpendicular, comoving magnetic field which oscillates at the same frequency, but with a phase shifted by 90°. they describe the movement of a packet of energy between two points. in the discussion of em waves, we are normally concerned with its wavelike behaviour. Electromagnetic waves propagate at the speed of light. light is an electromagnetic wave. there are other forms of electromagnetic radiation. those are the three important conclusions from this mathematical excursion. history. let's recall the steps that led to the formulation of maxwell's four laws.
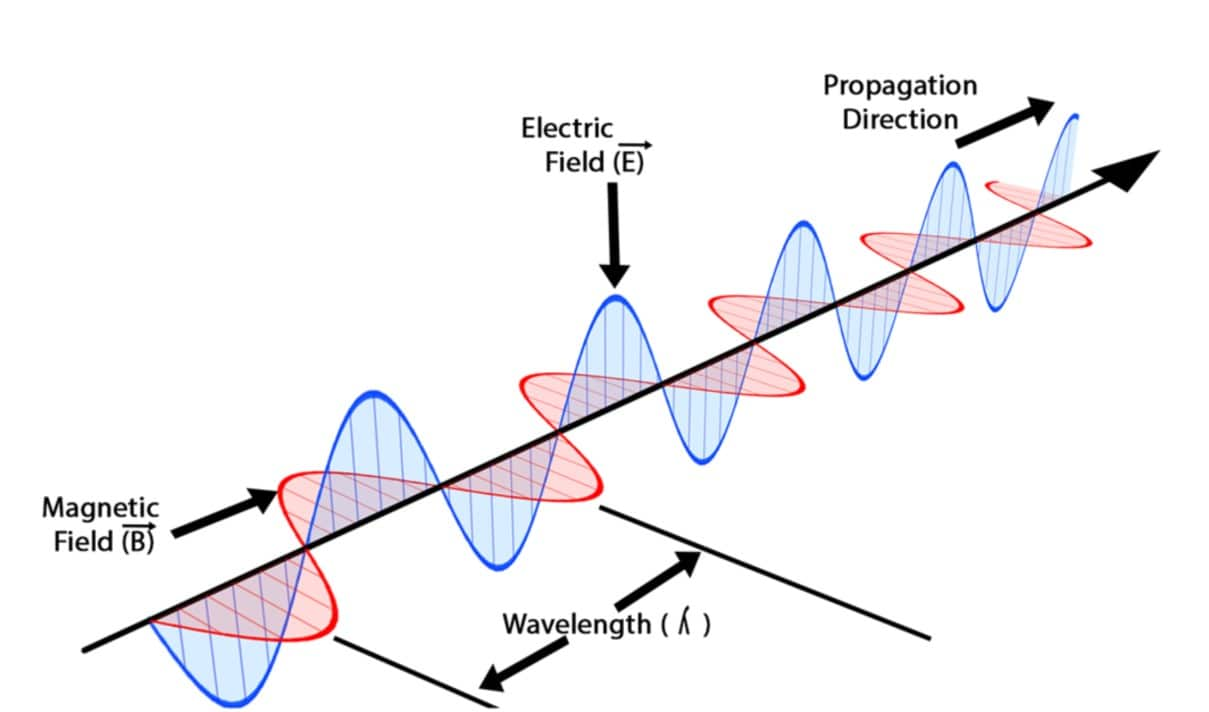
Electromagnetic Waves Definition Equation And Properties Of Electromagnetic waves have two components: an oscillating electric field and a perpendicular, comoving magnetic field which oscillates at the same frequency, but with a phase shifted by 90°. they describe the movement of a packet of energy between two points. in the discussion of em waves, we are normally concerned with its wavelike behaviour. Electromagnetic waves propagate at the speed of light. light is an electromagnetic wave. there are other forms of electromagnetic radiation. those are the three important conclusions from this mathematical excursion. history. let's recall the steps that led to the formulation of maxwell's four laws.
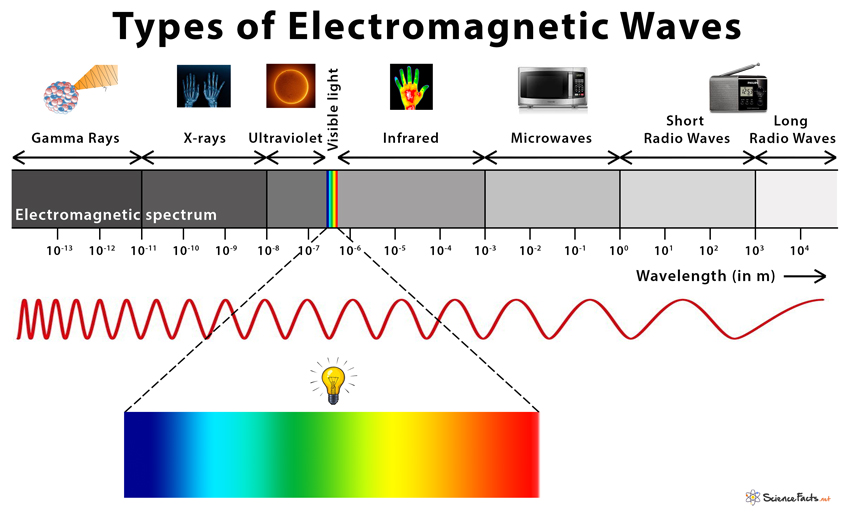
Electromagnetic Waves Classification Of Electromagnetic Wave

Comments are closed.