Force Applied At An Angle With Friction
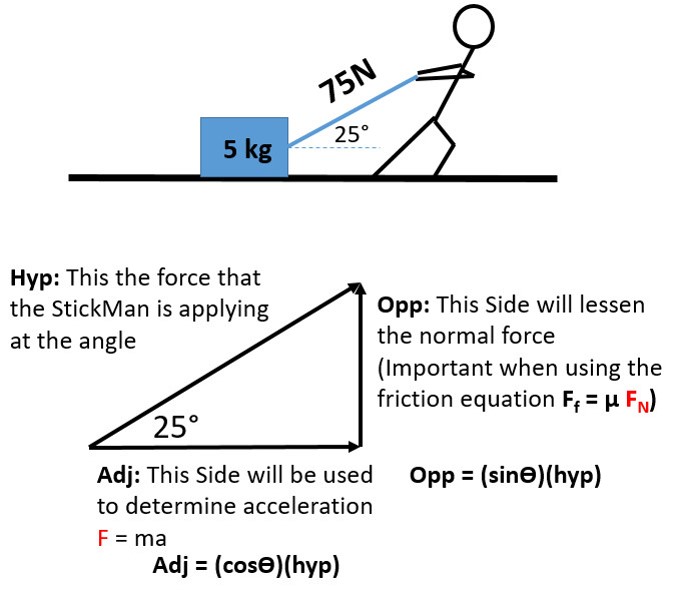
Frictional Force Static And Kinetic Friction Stickman Physics Force applied at an angle with friction is a common physics problem. this video shows how to solve problems with a coefficient of friction and an external fo. Forces acting at an angle (with friction) mc web mech2 9 2009 here as in leaflet 2.6, we consider forces that act at an angle, but this time including friction. workedexample1. a force of 18 n acts on a particle, of mass 7.5 kg, at an angle of 30 above the horizontal. the particle is on a rough horizontal plane.

Force Applied At An Angle With Friction Youtube Learn how to calculate work done by force applied at an angle in this physics video. Net force (f net) with friction on an incline and no applied force. parallel force minus friction is the net force creating acceleration. use the parallel force downhill. f ⸗ = (sinӨ)(mg) find friction substituting normal force. f f = µf n. f n = (cosӨ)(mg) f f = µ (cosӨ)(mg) net force is the parallel force down the hill minus the force. Diagramming forces on objects on level ground, where the applied force it as an angle. Figure 6.11 (a) the force of friction f → f → between the block and the rough surface opposes the direction of the applied force f →. f →. the magnitude of the static friction balances that of the applied force. this is shown in the left side of the graph in (c).
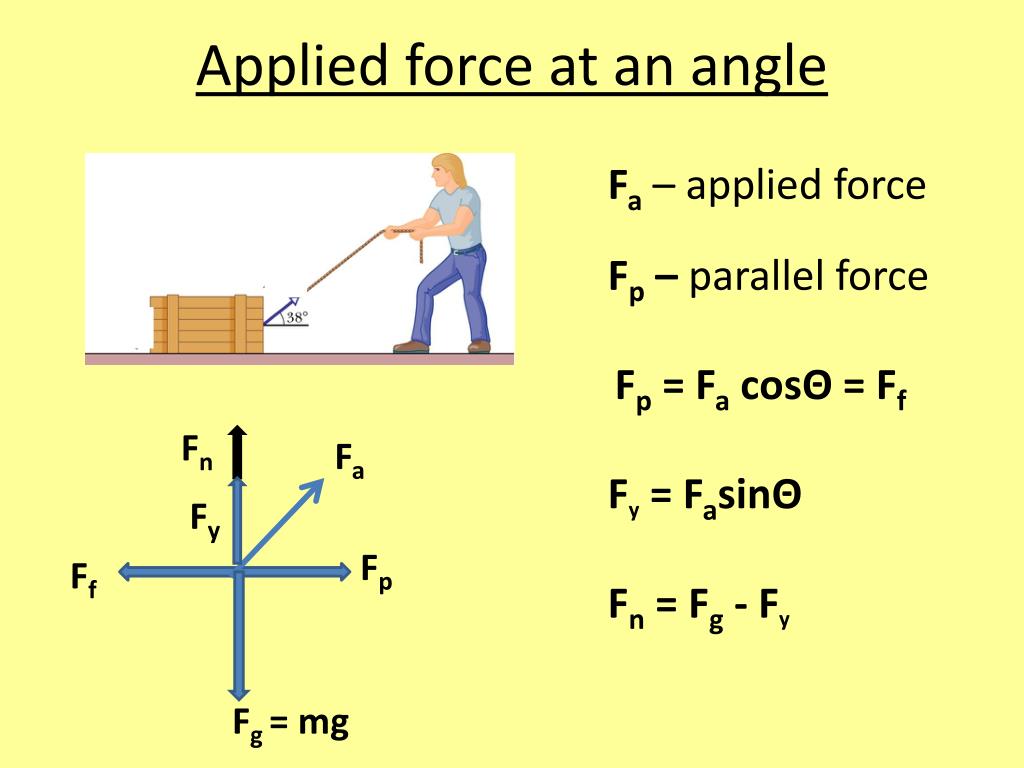
Force Applied At An Angle Formula Diagramming forces on objects on level ground, where the applied force it as an angle. Figure 6.11 (a) the force of friction f → f → between the block and the rough surface opposes the direction of the applied force f →. f →. the magnitude of the static friction balances that of the applied force. this is shown in the left side of the graph in (c). Types of friction. static friction: frictional force caused by an applied force at rest (before motion). kinetic sliding friction: frictional force when an object is sliding in motion. kinetic rolling friction: frictional force when an object is rubbing surfaces while rotating. from here, we will call kinetic sliding friction just kinetic. This is shown in the left side of the graph in (c). (b) at some point, the magnitude of the applied force is greater than the force of kinetic friction, and the block moves to the right. this is shown in the right side of the graph. (c) the graph of the frictional force versus the applied force; note that fs (max) > f k. this means that \(\mu.

Comments are closed.