Heating And Cooling Weathering Diagram
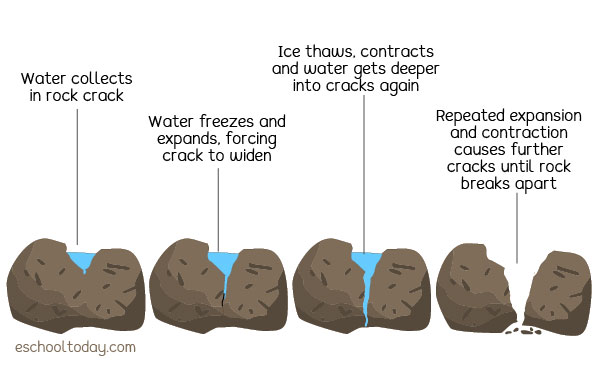
What Is The Physical Weathering Of Rocks вђ Eschooltoday The rock cycle is the natural, continuous process that forms, breaks down, and reforms rock through geological, chemical, and physical processes. through the cycle, rocks convert between igneous, metamorphic, and sedimentary forms. it is a dynamic system that recycles earth’s materials in different forms, from molten magma deep below the. Abstract. this chapter considers the various processes of rock weathering, starting with physical weathering processes (frost, wetting and drying, heating and cooling or insolation weathering, and salt weathering (haloclasty)). it then turns to a consideration of chemical weathering processes and to the remarkable increase of interest in.

Onion Skin Exfoliation Weathering Weathering is the breaking down or dissolving of rocks and minerals on earth's surface. once a rock has been broken down, a process called erosion transports the bits of rock and minerals away. water, acids, salt, plants, animals, and changes in temperature are all agents of weathering and erosion. 3.2 weathering. physical (mechanical) weathering processes: freeze thaw, heating cooling, salt crystal growth, pressure release (dilation), vegetation root action and chemical weathering processes: hydrolysis, hydration, and carbonation. weathering is the wearing away of material in situ, that is, where it is. 2.5.2 chemical weathering. chemically, the earth’s surface is a very reactive place.to begin with, in most places and at least at certain times the surface is an aqueous environment, and water is not only a very effective solvent in itself but also a necessary medium for a great many chemical reactions. Caused by temperature changes. thermal stress weathering comprises two main types, thermal shock and thermal fatigue. thermal stress weathering is an important mechanism in deserts, where there is a large diurnal temperature range, hot in the day and cold at night. the repeated heating and cooling exerts stress on the outer layers of rocks,.
Diagram Of Weathering 2.5.2 chemical weathering. chemically, the earth’s surface is a very reactive place.to begin with, in most places and at least at certain times the surface is an aqueous environment, and water is not only a very effective solvent in itself but also a necessary medium for a great many chemical reactions. Caused by temperature changes. thermal stress weathering comprises two main types, thermal shock and thermal fatigue. thermal stress weathering is an important mechanism in deserts, where there is a large diurnal temperature range, hot in the day and cold at night. the repeated heating and cooling exerts stress on the outer layers of rocks,. Mechanical physical weathering physical disintegration of a rock into smaller fragments, each with the same properties as the original. occurs mainly by temperature and pressure changes. chemical weathering process by which the internal structure of a mineral is altered by the addition or removal of elements. Weathering, needless to say, is an important environmental process that bridges all elements of our physical environment and sustains the notion of a changing earth. figure 12.1.1 12.1. 1: talus slopes created by physical weathering. (courtesy usgs dds21) weathering occurs in two ways.

Comments are closed.