Marine Ecology Intro And Patterns In The Marine Environment

Marine Ecology Intro And Patterns In The Marine Environment Youtube This is a voice narrated powerpoint lecture recorded for my florida gulf coast university marine ecology course. this one is intended to be the first lecture. The best documented patterns in marine biodiversity refer to decreased species richness from shallow to deep water. this pattern arises from the historical “azoic theory” proposed in the mid xix century by e. forbes who proposed that the harsh environmental conditions of the deep sea would reduce species persistence.
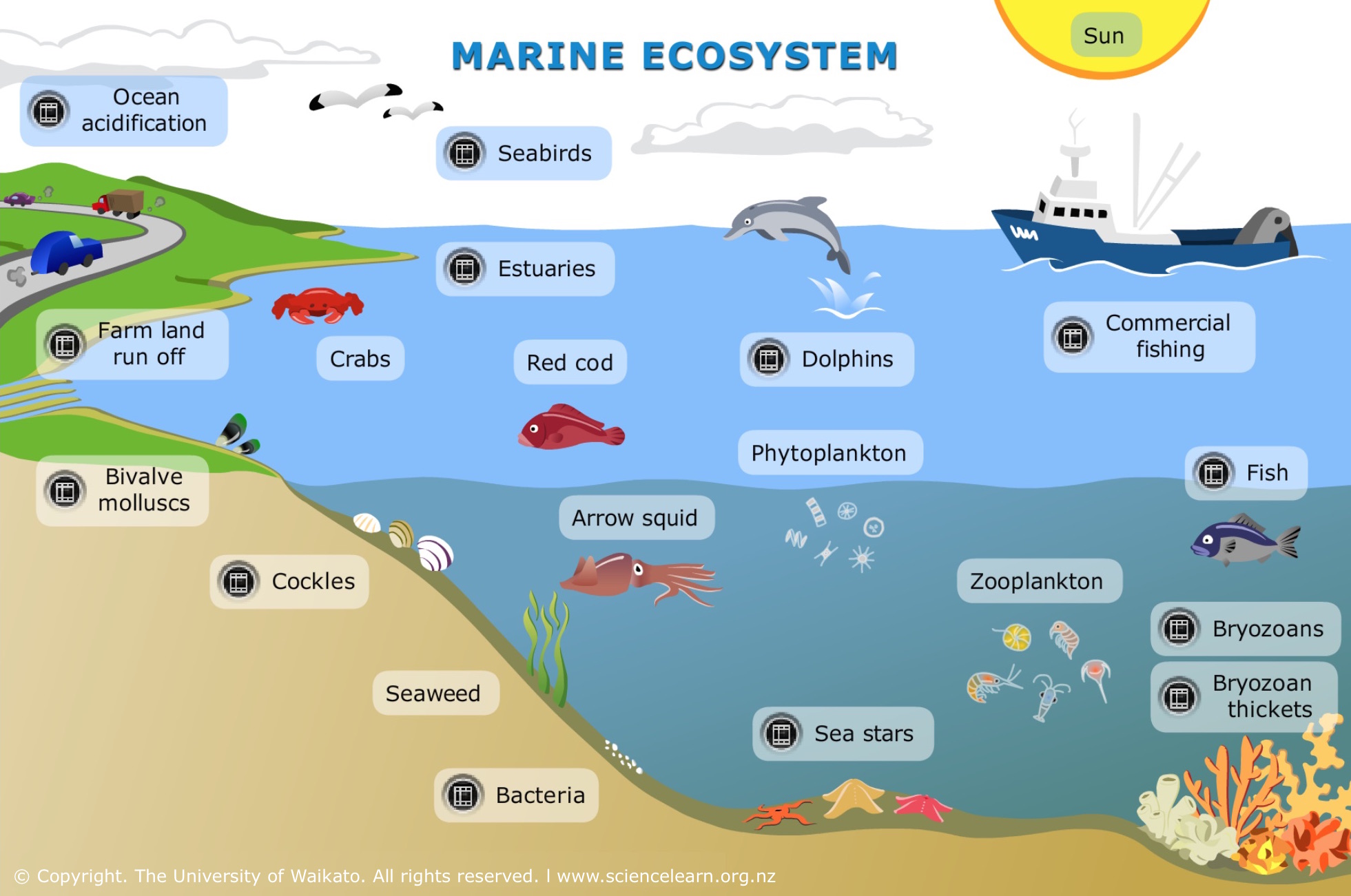
Primary Consumers Of The Ocean Marine ecology is the scientific study of marine life habitats, populations, and interactions among organisms and the surrounding environment including their abiotic (non living physical and chemical factors that affect the ability of organisms to survive and reproduce) and biotic factors (living things or the materials that directly or. Patterns and processes influencing the structure of marine assemblages. in marine ecosystem. also known as: ocean ecosystem, sea ecosystem. written by. michael john kingsford. professor and head of the school of marine biology and aquaculture, james cook university, queensland, australia. michael john kingsford. fact checked by. Marine ecosystem, complex of living organisms in the ocean environment. marine waters cover two thirds of the surface of the earth. in some places the ocean is deeper than mount everest is high; for example, the mariana trench and the tonga trench in the western part of the pacific ocean reach depths in excess of 10,000 metres (32,800 feet). Course description. this course provides an introduction to ecology, covering interactions between marine organisms and the environment at scales of populations, communities, and ecosystems. the course culminates with a field based research project with students working in the intertidal zone of appledore island and test concepts and theories.

The Marine Environment Ecology Management And Conservation вђ Nova Marine ecosystem, complex of living organisms in the ocean environment. marine waters cover two thirds of the surface of the earth. in some places the ocean is deeper than mount everest is high; for example, the mariana trench and the tonga trench in the western part of the pacific ocean reach depths in excess of 10,000 metres (32,800 feet). Course description. this course provides an introduction to ecology, covering interactions between marine organisms and the environment at scales of populations, communities, and ecosystems. the course culminates with a field based research project with students working in the intertidal zone of appledore island and test concepts and theories. Marine ecosystems are aquatic environments with high levels of dissolved salt, such as those found in or near the ocean. marine ecosystems are defined by their unique biotic (living) and abiotic (nonliving) factors. biotic factors include plants, animals, and microbes; important a biotic factors include the amount of sunlight in the ecosystem. Marine ecosystems. the earth is a blue planet. seas and oceans cover over 70% of the earth's surface and, with an average depth of over 3.2 km, the total volume of marine ecosystems is vastly greater than that of terrestrial and fresh water environments combined, comprising 98% of the total inhabitable space on the planet (speight and henderson.

Comments are closed.