Motion In Two Dimension Motion In A Plane Part 3 Plus One Physics

Motion In Two Dimension Motion In A Plane Part 3 Plus One Physics 4.2.2 equality of vectors. 4.3 multiplication of vectors by real numbers. 4.4 addition and subtraction of vectors — graphical method. 4.5 resolution of vectors. 4.6 vector addition – analytical method. 4.7 motion in a plane. 4.7.1 position vector and displacement. 4.8 motion in a plane with constant acceleration. 4.9 relative velocity in. 4.5 resolution of vectors. let a and b be any two non zero vectors in a plane with different directions and let a be another vector in the same plane(fig. 4.8). a can be expressed as a sum of two vectors – one obtained by multiplying a by a real number and the other obtained by multiplying b by another real number.

Physics 2 Dimensional Motion Topics and subtopics in ncert solutions for class 11 physics chapter 4 motion in a plane: questions from textbook. question 4. 1. state, for each of the following physical quantities, if it is a scalar or a vector: volume, mass, speed, acceleration, density, number of moles, velocity, angular frequency, displacement, angular velocity. answer. Projectile motion is one of the most common examples of motion in a plane. in projectile motion, the only acceleration acting is in the vertical direction, which is acceleration due to gravity (g). therefore, equations of motion can be applied separately in x axis and y axis to find the unknown parameters. Motion in a plane class 11 notes physics chapter 4. • motion in a plane is called as motion in two dimensions e.g., projectile motion, circular motion etc. for the analysis of such motion our reference will be made of an origin and two co ordinate axes x and y. • scalar and vector quantities. scalar quantities. Kerala plus one physics chapter wise previous questions and answers. chapter 1 physical world. chapter 2 units and measurement. chapter 3 motion in a straight line. chapter 4 motion in a plane. chapter 5 law of motion. chapter 6 work, energy and power. chapter 7 systems of particles and rotational motion. chapter 8 gravitation.
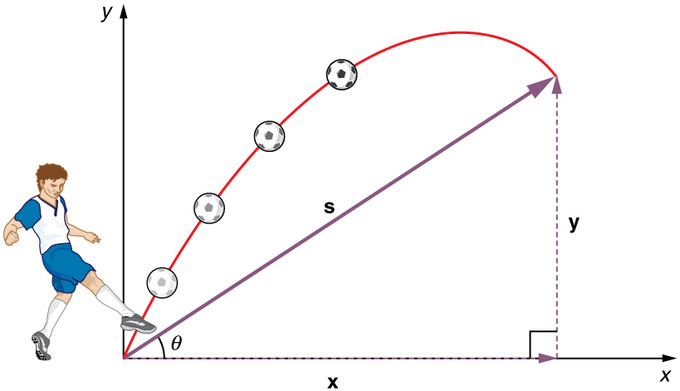
Motion In Two Dimensions Boundless Physics Motion in a plane class 11 notes physics chapter 4. • motion in a plane is called as motion in two dimensions e.g., projectile motion, circular motion etc. for the analysis of such motion our reference will be made of an origin and two co ordinate axes x and y. • scalar and vector quantities. scalar quantities. Kerala plus one physics chapter wise previous questions and answers. chapter 1 physical world. chapter 2 units and measurement. chapter 3 motion in a straight line. chapter 4 motion in a plane. chapter 5 law of motion. chapter 6 work, energy and power. chapter 7 systems of particles and rotational motion. chapter 8 gravitation. Figure 5.29 (a) we analyze two dimensional projectile motion by breaking it into two independent one dimensional motions along the vertical and horizontal axes. (b) the horizontal motion is simple, because a x = 0 a x = 0 and v x v x is thus constant. The vector equation is →vpg = →vpa →vag, where p = plane, a = air, and g = ground. from the geometry in figure 4.6.6, we can solve easily for the magnitude of the velocity of the plane with respect to the ground and the angle of the plane’s heading, θ. figure 4.6.6: vector diagram for equation 4.6.2 showing the vectors →vpa, →vag.

Comments are closed.