Reciprocal Trigonometric Functions Cosecant Secant And Cotangent

Reciprocal Trigonometric Functions Cosecant Secant Cotangent You Reciprocal identities are the reciprocals of the six main trigonometric functions, namely sine, cosine, tangent, cotangent, secant, cosecant. the important thing to note is that reciprocal identities are not the same as the inverse trigonometric functions. Evaluate the reciprocal trig functions for angles in degrees or radians; find values or expressions for the six trig ratios; evaluate the reciprocal trig functions in applications; given one trig ratio, find the others; evaluate expressions exactly; graph the secant, cosecant, and cotangent functions; identify graphs of the reciprocal trig.

The Other Three Trig Ratios Blackman High School The abbreviation of cosecant is csc or cosec. the cotangent function is the reciprocal of the tangent function. the abbreviation of cotangent is cot. the following diagram shows the reciprocal trigonometric functions. scroll down the page for more examples and solutions on how to use the reciprocal trigonometric functions. 3 evaluate the reciprocal trig functions in applications #29–32. 4 given one trig ratio, find the others #33–46, 71–80. 5 evaluate expressions exactly #47–52. 6 graph the secant, cosecant, and cotangent functions #53–58. 7 identify graphs of the reciprocal trig functions #59–64. 8 solve equations in secant, cosecant, and cotangent. The first one is a reciprocal: csc θ = 1 sin θ. \displaystyle \csc {\ }\theta=\frac {1} { { \sin {\ }\theta}} csc θ = sin θ1 . . the second one involves finding an angle whose sine is θ. so on your calculator, don't use your sin 1 button to find csc θ. we will meet the idea of sin 1θ in the next section, values of trigonometric. In trigonometry, reciprocal identities are sometimes called inverse identities. reciprocal identities are inverse sine, cosine, and tangent functions written as “arc” prefixes such as arcsine, arccosine, and arctan. for instance, functions like sin^ 1 (x) and cos^ 1 (x) are inverse identities. either notation is correct and acceptable.
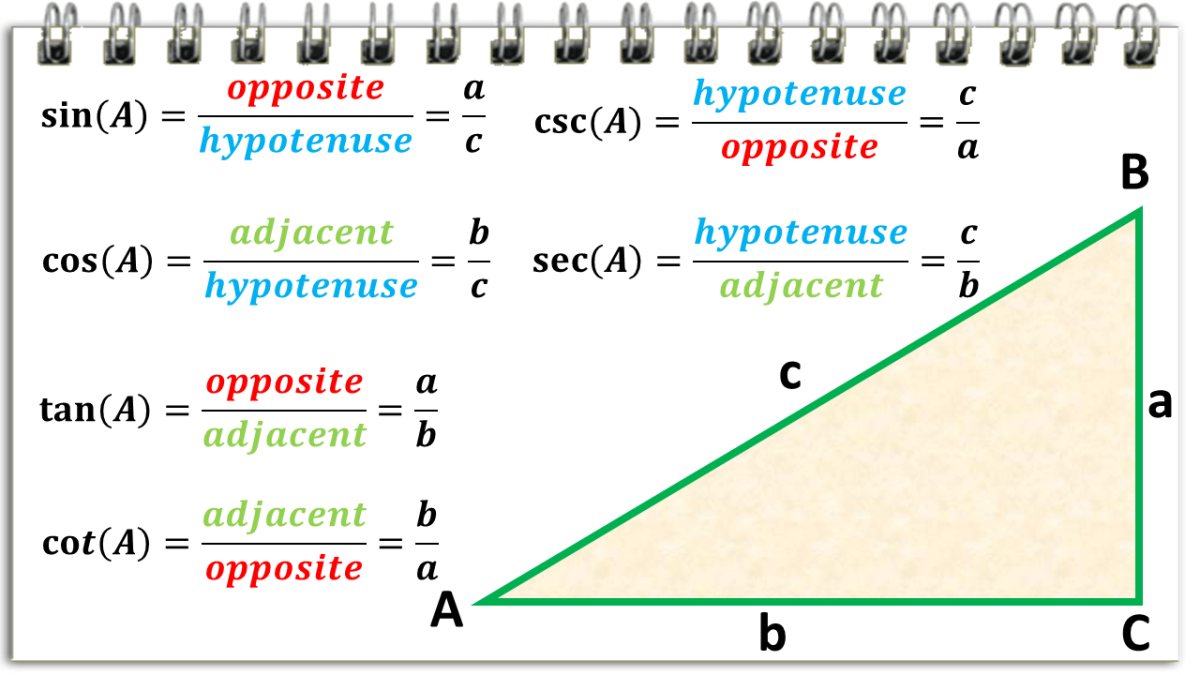
Reciprocal Identities In Trigonometry With Examples Owlcation The first one is a reciprocal: csc θ = 1 sin θ. \displaystyle \csc {\ }\theta=\frac {1} { { \sin {\ }\theta}} csc θ = sin θ1 . . the second one involves finding an angle whose sine is θ. so on your calculator, don't use your sin 1 button to find csc θ. we will meet the idea of sin 1θ in the next section, values of trigonometric. In trigonometry, reciprocal identities are sometimes called inverse identities. reciprocal identities are inverse sine, cosine, and tangent functions written as “arc” prefixes such as arcsine, arccosine, and arctan. for instance, functions like sin^ 1 (x) and cos^ 1 (x) are inverse identities. either notation is correct and acceptable. If you're seeing this message, it means we're having trouble loading external resources on our website. if you're behind a web filter, please make sure that the domains *.kastatic.org and *.kasandbox.org are unblocked. Reciprocal identities involve six trigonometric functions: sine (sin), cosine (cos), tangent (tan), cosecant (csc), secant (sec), and cotangent (cot). the reciprocal identities show that the ratio of one function to its reciprocal is always equal to 1. for instance, the sine and cosecant reciprocal identities: sin (θ) = 1 csc (θ) and csc (θ.
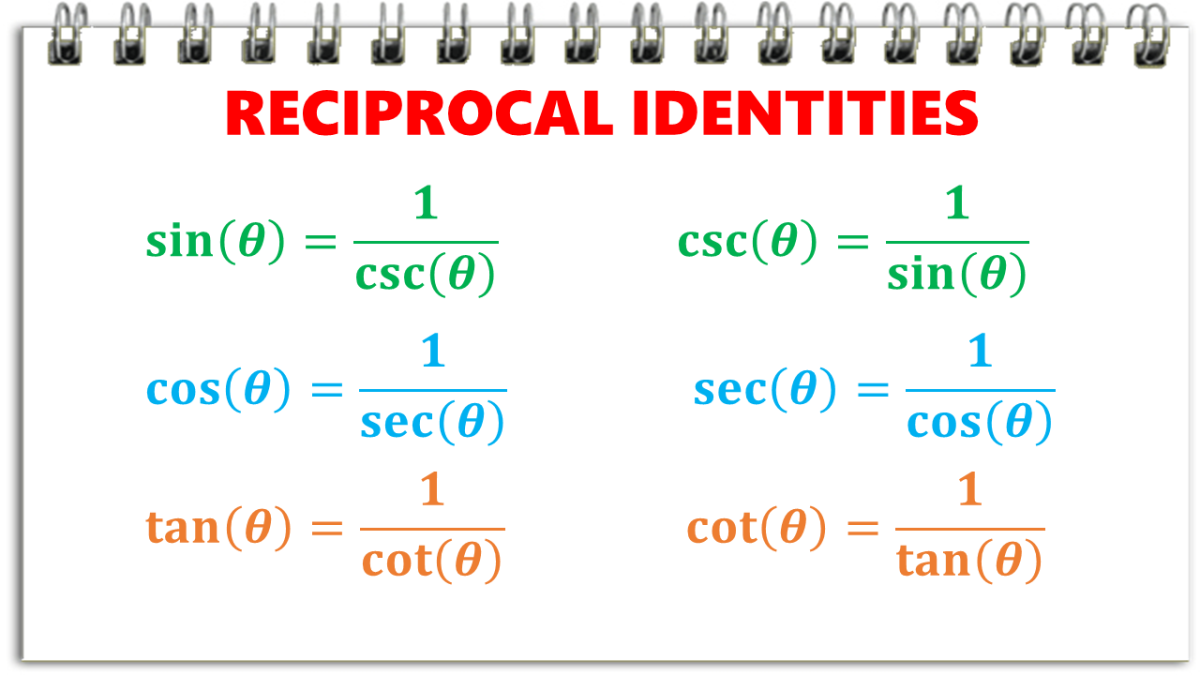
Reciprocal Identities In Trigonometry With Examples Owlcation If you're seeing this message, it means we're having trouble loading external resources on our website. if you're behind a web filter, please make sure that the domains *.kastatic.org and *.kasandbox.org are unblocked. Reciprocal identities involve six trigonometric functions: sine (sin), cosine (cos), tangent (tan), cosecant (csc), secant (sec), and cotangent (cot). the reciprocal identities show that the ratio of one function to its reciprocal is always equal to 1. for instance, the sine and cosecant reciprocal identities: sin (θ) = 1 csc (θ) and csc (θ.
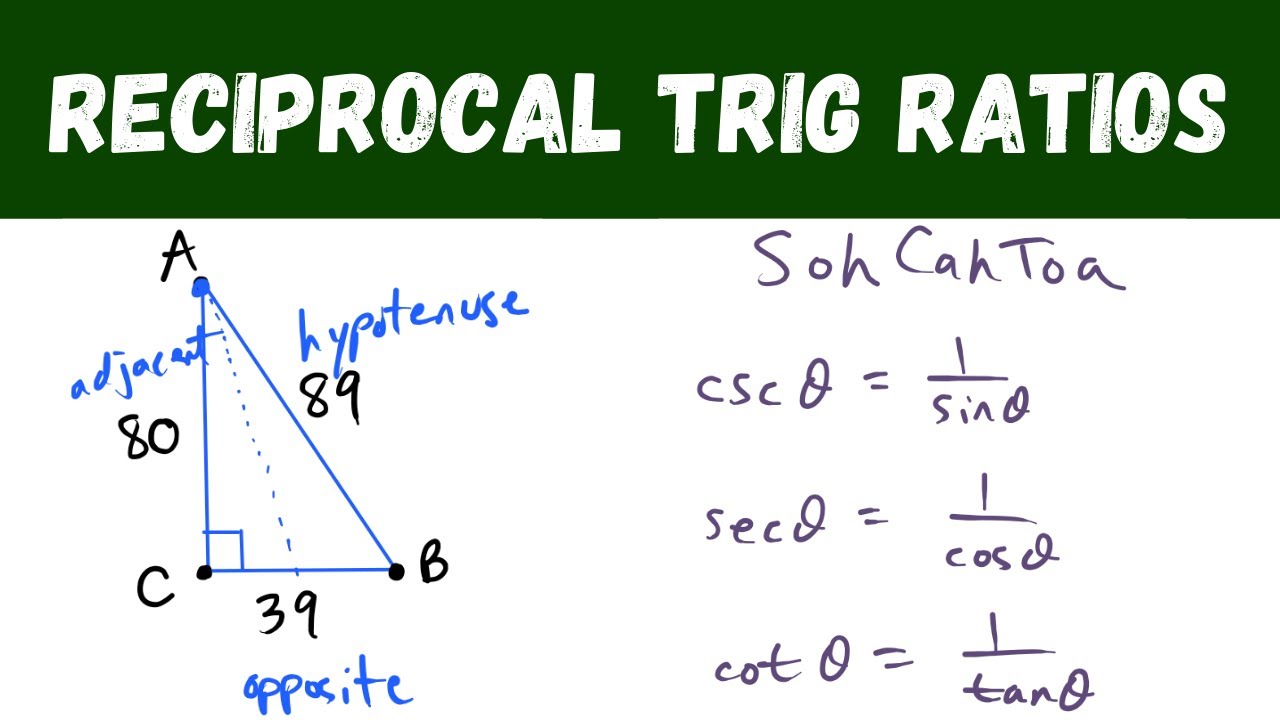
Reciprocal Trig Ratios Sine Cosine Tangent Cosecant Secant

Comments are closed.