The Cardiac Cycle 2

Cardiac Cycle Definition Phases And Quiz Biology Dictionary Cardiac cycle phases. the events of the cardiac cycle, start with a spontaneous action potential in the sinus node as we described previously. this stimulus causes a series of events in the atria and the ventricles. all these events are “organized” in two phases: diastole (when the heart fills with blood) and systole (when the heart pumps. The cardiac cycle is complete. figure 19.3.2 illustrates the relationship between the cardiac cycle and the ecg. figure 19.3.2 – relationship between the cardiac cycle and ecg: initially, both the atria and ventricles are relaxed (diastole). the p wave represents depolarization of the atria and is followed by atrial contraction (systole).
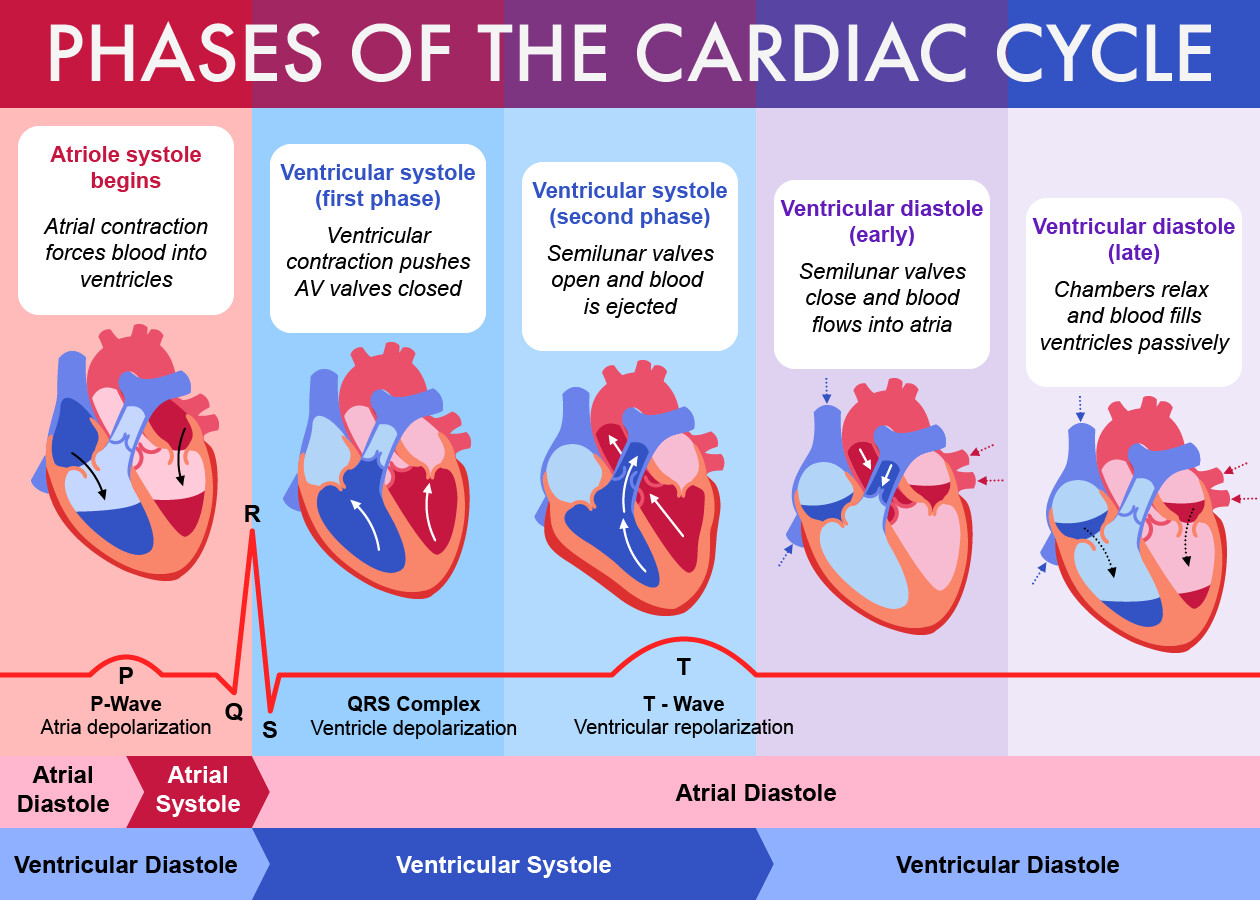
Artstation Phases Of The Cardiac Cycle The cardiac cycle is a series of pressure changes within the heart. these pressure changes result in blood movement through different chambers of the heart and the body as a whole. these pressure changes originate as conductive electrochemical changes within the myocardium that result in the concentric contraction of cardiac muscle. valves within the heart direct blood movement, which leads to. [1] [2] throughout the cardiac cycle, blood pressure increases and decreases. the movements of cardiac muscle are coordinated by a series of electrical impulses produced by specialized pacemaker cells found within the sinoatrial node and the atrioventricular node. cardiac muscle is composed of myocytes which initiate their internal contractions. The cardiac cycle comprises a complete relaxation and contraction of both the atria and ventricles, and lasts approximately 0.8 seconds. beginning with all chambers in diastole, blood flows passively from the veins into the atria and past the atrioventricular valves into the ventricles. The cardiac cycle can be divided into four stages: filling phase – the ventricles fill during diastole and atrial systole. isovolumetric contraction – the ventricles contract, but as the heart valves are shut, the volume remains constant. this causes a build up of pressure, ready to propel blood into the aorta pulmonary trunk.

Comments are closed.